介绍Iym
当臭氧空洞在1984年被发现(中钵,1984;法曼et al ., 1985),在南极洲担心紫外线辐射水平上升。紫外线辐射并不是衡量在南极洲,促使美国国家科学基金会(NSF)建立紫外线监控程序,现在被称为“NSF紫外光谱辐照度监测网络(UVSIMN)”(Booth et al., 1994). Similar monitoring activities also commenced in the 1980s and 1990s in Canada (Fioletov et al., 2001), Europe (e.g., Gröbner et al., 2006), New Zealand (McKenzie et al., 1999), the United States (Kaye et al., 1999), and other regions. The UVSIMN network currently consists of six sites at high latitudes and a system at San Diego, California. It has been operated byBiospherical仪器公司。自1988年以来(BSI)。网站提供的概述在表3.1和图3.1。程序采用suv - 100和suv - 150 b用衡量全球280 nm和600 nm之间的光谱辐照度约1.0纳米的带通(suv - 100)或0.63 nm (suv - 150 b)半宽度(应用)。结果在大约100个同行评议的出版物以及用于科学评估臭氧损耗由世界气象组织发布(如世界气象组织,2007)。引用的完整列表和额外的信息网络可以在操作报告(例如,Bernhard et al ., 2006),在项目的网站http://www.biospherical.com/NSF。
表3.1网站
网站
经度纬度海拔建立用于研究
南极,南极90°00 - 2841 m
南极洲麦克默多,77°50 166°40本部183米
帕默,南极洲64°46 64°03 'w 21米
阿根廷乌斯怀亚54°49 68°19 'w 25米
加州圣地亚哥32°46 117°12镑'w 22米
阿拉斯加巴罗,71°19 156°41 'w 8镑
峰会上,格陵兰岛72°35 38°27 'w 3200镑
1988年2月1991年1月- 2007年1月
1988年3月1989年12月- 2007年1月
1990年3月1988年5月——2006年4月
1988年11月1988年11月- 2005年6月
1992年10月1992年10月- 2006年8月
1990年12月1991年1月- 2007年4月
2004年8月2004年8月- 2006年11月
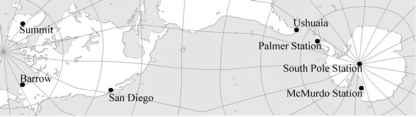
图3.1 UVSIMN地图网站(由Eric Gaba基于富勒地图)。竖线表示纬度0°±20°,±40°,±60°。(Fuller投影地图巴克明斯特·富勒研究所的设计是一个商标©1938年,1967年和1992年。版权所有,http://www.bfi.org)
图3.1 UVSIMN地图网站(由Eric Gaba基于富勒地图)。竖线表示纬度0°±20°,±40°,±60°。(Fuller投影地图巴克明斯特·富勒研究所的设计是一个商标©1938年,1967年和1992年。版权所有,http://www.bfi.org)
在这一章,紫外线辐射的气候学UVSIMN网站。紫外线辐射在高纬度网站不同于在低纬度地区由于小型太阳能海拔条件;24小时在春季和夏季的阳光;长时间的黑暗冬季;南极上空臭氧层空洞每年发生严重的北极上空的臭氧损耗和最近的事件;从全年季节性或表面反照率高冰雪覆盖;小在南极洲和格陵兰岛的内部云的影响由于大气水含量较低;和小气溶胶光学深度。紫外线辐射发生巨大变化,由于臭氧空洞可以预期,但其他因素也很重要。然而,紫外线测量的基础上确认趋势UVSIMN仍然遥遥无期。通过分析测量南极,帕默,麦克默多,Bernhard et al。(2004;2005;2006 b)得出的结论是,线性趋势估计在95.5%置信水平总的来说不重要。显著的线性趋势观察只有2月和3月个月的麦克默多(由于云的变化和/或反照率),以及2月在帕默。有几个因素导致了这一发现:(1)网络的操作开始后仅在1980年代末臭氧层空洞已经被观察到; (2) time-series of about 15 - 18 years are still considered short for reliable trend detection (Weatherhead et al., 1998); (3) there is a large year-to-year variability in total ozone, cloudiness, and albedo at most network sites, which obstructs the detection of possible long-term changes; (4) measurement uncertainties affect the detection of trends; and (5) the stratospheric chlorine loading (and the potential for ozone depletion) was highest at the turn of the century (WMO, 2007), approximately in the middle of UVSIMN time-series. The last factor suggests that changes in UV radiation over the period of UVSIMN operations should be described with a second-order rather than a linear function. In addition to the availability of ozone-depleting chemicals, the depth and extent of the ozone hole is also largely controlled by meteorology,行星波活动,以及平流层气温(雷克斯et al ., 2004;世界气象组织,2007年)。这些因素显示每年的巨大变化。,尽管有这些可变性最大的紫外线强度在南国UVSIMN地点观察在1997年和1998年时候平流层氯浓度最大(Bernhard et al ., 2004, 2005, 2006 b)。虽然我们不尝试趋势估计在这项研究中,我们估计过去紫外线水平五个网站从历史臭氧总量的测量,从近期建立的气候学与这些估计测量UVSIMN。这种分析文件大南极紫外线气候的变化,发生在过去的40年。raybet雷竞技最新
继续阅读:历史紫外线指数的估计
这篇文章有用吗?